;
bag.clear();
cout << “”isEmpty: returns “” << bag.isEmpty()
<< “”; should be 1 (true)”” << endl;
} // end bagTester
int main()
{
DLinkedBag bag;
cout << “”Testing the Link-Based Bag:”” << endl;
cout << “”The initial bag is empty.”” << endl;
bagTester(bag);
cout << “”All done!”” << endl;
return 0;
} // end main
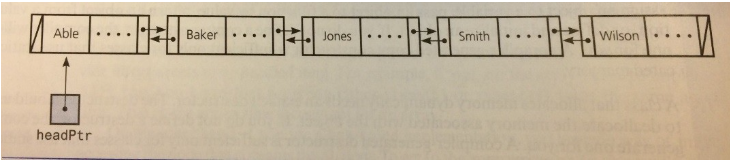
In a doubly linked list, each node can point to the previous node as well as to the next node. Figure 4-10 shows a doubly linked list and its head pointer. Define a class DoublyLinkedBag using C++ that implements the ADT bag by using a doubly linked list as shown in Figure 4-10.
[Hint: you need to define a class to represent a node in a doubly linked list by modifying the node class we used for linked base implementation of ADT Bag]
Requirement:
+ Create the header DLinkedBag.h to implemented ADT Bag.
+ Use the following program to test your ADT Bag implemented by doubly linked list.
// This program tests the ADT Bag class which is implemented by a doubly
// linked list.
#include
#include
#include “DLinkedBag.h” //doubly linked list bag
using namespace std;
void displayBag(const DLinkedBag& bag)
{
cout << “The bag contains ” << bag.getCurrentSize()
<< ” items:” << endl;
vector bagItems = bag.toVector();
int numberOfEntries = (int)bagItems.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfEntries; i++)
{
cout << bagItems[i] << ” “;
} // end for
cout << endl << endl;
} // end displayBag
void bagTester(DLinkedBag& bag)
{
cout << “isEmpty: returns ” << bag.isEmpty()
<< “; should be 1 (true)” << endl;
displayBag(bag);
string items[] = { “one”, “two”, “three”, “four”, “five”, “one” };
cout << “Add 6 items to the bag: ” << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
bag.add(items[i]);
} // end for
displayBag(bag);
cout << “isEmpty: returns ” << bag.isEmpty()
<< “; should be 0 (false)” << endl;
cout << “getCurrentSize: returns ” << bag.getCurrentSize()
<< “; should be 6” << endl;
cout << “Try to add another entry: add(“extra””) returns “”
<< bag.add(“”extra””) << endl;
cout << “”contains(“”three””): returns “” << bag.contains(“”three””)
<< “”; should be 1 (true)”” << endl;
cout << “”contains(“”ten””): returns “” << bag.contains(“”ten””)
<< “”; should be 0 (false)”” << endl;
cout << “”getFrequencyOf(“”one””): returns “”
<< bag.getFrequencyOf(“”one””) << “” should be 2″” << endl;
cout << “”remove(“”one””): returns “” << bag.remove(“”one””)
<< “”; should be 1 (true)”” << endl;
cout << “”getFrequencyOf(“”one””): returns “”
<< bag.getFrequencyOf(“”one””) << “” should be 1″” << endl;
cout << “”remove(“”one””): returns “” << bag.remove(“”one””)
<< “”; should be 1 (true)”” << endl;
cout << “”remove(“”one””): returns “” << bag.remove(“”one””)
<< “”; should be 0 (false)”” << endl;
cout << endl;
displayBag(bag);
cout << “”After clearing the bag
bag.clear();
cout << “”isEmpty: returns “” << bag.isEmpty()
<< “”; should be 1 (true)”” << endl;
} // end bagTester
int main()
{
DLinkedBag bag;
cout << “”Testing the Link-Based Bag:”” << endl;
cout << “”The initial bag is empty.”” << endl;
bagTester(bag);
cout << “”All done!”” << endl;
return 0;
} // end main

 Talk to us support@bestqualitywriters.com
Talk to us support@bestqualitywriters.com